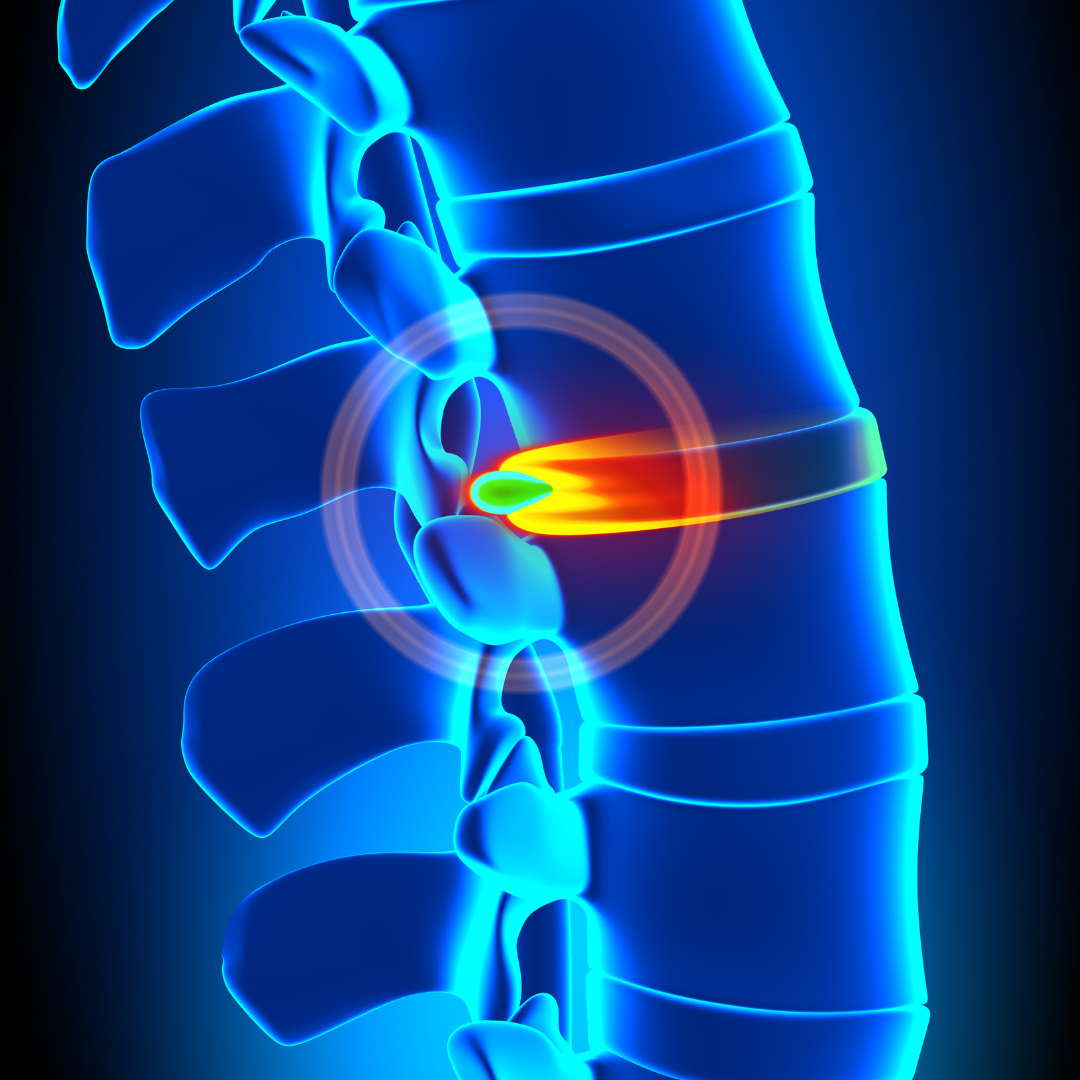
The spine is made up of a series of bones, called vertebrae, that are stacked on top of one another. In between each of these vertebrae, there are soft, spongy discs that act as cushions or shock absorbers, helping to protect the spinal cord and nerves.
A spinal disc injury occurs when there is damage or trauma to one or more of these discs. This can cause the disc to herniate or rupture, which can put pressure on the surrounding nerves and cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area.
Spinal disc injuries can have a number of different causes. Some of the most common causes include:
-
Age-related degeneration: As we get older, the discs in our spine can naturally wear down and become less flexible, making them more prone to injury.
-
Trauma: A sudden impact or injury to the spine, such as a fall or car accident, can cause a disc injury.
-
Poor posture: Sitting or standing in the same position for extended periods can cause stress on the discs in the spine, which can lead to injury over time.
-
Repetitive motion: Doing the same motion over and over again, such as lifting heavy objects or playing certain sports, can cause disc injury.
-
Genetics: Some people may be more prone to disc injury due to genetic factors.
It's important to note that while spinal disc injuries can be painful and debilitating, there are a variety of treatments available to help manage the symptoms and promote healing. If you think you may have a spinal disc injury, it's important to seek medical attention to determine the best course of treatment for your specific situation.
Understanding 6 disc injuries in the spine:
-
Disc herniation: This occurs when the soft inner core of the disc pushes out through a crack in the outer layer, putting pressure on nearby nerves. This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area. Disc herniation is most common in the lower back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine).
-
Disc bulge: This is similar to a herniation, but the outer layer of the disc is not completely torn. Instead, the disc bulges out of its normal space, putting pressure on nearby nerves. Symptoms can include pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area.
-
Disc degeneration: This is a natural part of the aging process, in which the discs in the spine lose some of their water content, becoming less flexible and more prone to injury. Disc degeneration can cause pain and stiffness in the affected area.
-
Disc tear: This occurs when the outer layer of the disc is torn, causing pain and inflammation in the affected area.
-
Disc desiccation: This is another term for disc degeneration, in which the discs lose their water content and become less flexible.
-
Disc sequestration: This is a rare but serious type of disc injury, in which the inner core of the disc breaks away and becomes a free-floating fragment in the spinal canal. This can cause severe pain and neurological symptoms and may require surgical intervention.